Urinalysis is a common diagnostic test that provides valuable insights into your overall health by examining the physical, chemical, and microscopic properties of your urine. It’s a quick, non-invasive way to screen for various conditions, from urinary tract infections to kidney disease and diabetes.
If you’ve had a urinalysis and received your results, you might wonder what the numbers and terms mean. Here’s a detailed guide to help you understand the components of a urinalysis and what your results might indicate.
What is a Urinalysis Test?
Urinalysis is typically performed for three main purposes:
- Screening: To detect conditions in their early stages.
- Diagnosis: To confirm or rule out a suspected health issue.
- Monitoring: To track the progress of a condition or the effectiveness of treatment.
The test involves analyzing urine samples across three categories: physical appearance, chemical composition, and microscopic examination.
Key Components of a Urinalysis and Their Significance
1. Physical Appearance
- Color:
- Normal: Pale yellow to amber.
- Abnormal:
- Dark yellow or brown: May indicate dehydration or liver disease.
- Red or pink: Could suggest blood in the urine, possibly due to infection, kidney stones, or trauma.
- Cloudy: May indicate infection or the presence of pus, mucus, or crystals.
- Clarity:
- Normal: Clear.
- Abnormal: Cloudy urine may suggest an infection or high levels of certain substances like protein or white blood cells.
- Odor:
- Strong, unusual odors might indicate an infection, diabetes (sweet smell due to ketones), or certain foods like asparagus.
2. Chemical Analysis
A chemical strip is dipped into the urine to test for the following:
- pH (Acidity/Alkalinity):
- Normal Range: 4.5–8.0.
- Low pH (Acidic): May occur with a high-protein diet, diabetes, or diarrhea.
- High pH (Alkaline): May suggest kidney stones, UTIs, or a vegetarian diet.
- Protein:
- Normal: Minimal or none detected.
- Abnormal: High protein levels (proteinuria) could indicate kidney disease, high blood pressure, or infection.
- Glucose:
- Normal: None detected.
- Abnormal: Presence of glucose may indicate diabetes or high blood sugar levels.
- Ketones:
- Normal: None detected.
- Abnormal: Ketones may appear in cases of uncontrolled diabetes, starvation, or extreme low-carb diets.
- Bilirubin:
- Normal: None detected.
- Abnormal: Presence may indicate liver disease or bile duct obstruction.
- Nitrites:
- Normal: None detected.
- Abnormal: Positive nitrites suggest a bacterial UTI.
- Leukocyte Esterase:
- Normal: None detected.
- Abnormal: Indicates white blood cells in the urine, often a sign of infection.
- Blood:
- Normal: None or trace amounts.
- Abnormal: Blood in urine (hematuria) could be due to infections, kidney stones, trauma, or more serious conditions like cancer.
3. Microscopic Examination
This part of the test looks for substances not typically visible to the naked eye.
- Red Blood Cells (RBCs):
- Normal: 0–4 per high power field (HPF).
- Abnormal: High levels could indicate injury, infection, kidney disease, or stones.
- White Blood Cells (WBCs):
- Normal: 0–5 per HPF.
- Abnormal: Elevated levels suggest infection or inflammation.
- Casts:
- Normal: Few or none.
- Abnormal: Different types of casts (hyaline, granular, red blood cell casts) may indicate kidney disease or other conditions.
- Crystals:
- Normal: Few or none.
- Abnormal: Certain crystals may suggest kidney stones or metabolic disorders.
- Bacteria, Yeast, or Parasites:
- Normal: None detected.
- Abnormal: Their presence typically indicates an infection.
What to Do if Your Results are Abnormal
Abnormal urinalysis results don’t always mean something serious. Temporary factors like dehydration, diet, or exercise can affect your test. If your results are outside the normal range:
- Discuss them with your doctor.
- Follow up with additional tests if necessary.
- Make lifestyle changes if recommended, such as staying hydrated, eating a balanced diet, or managing chronic conditions.
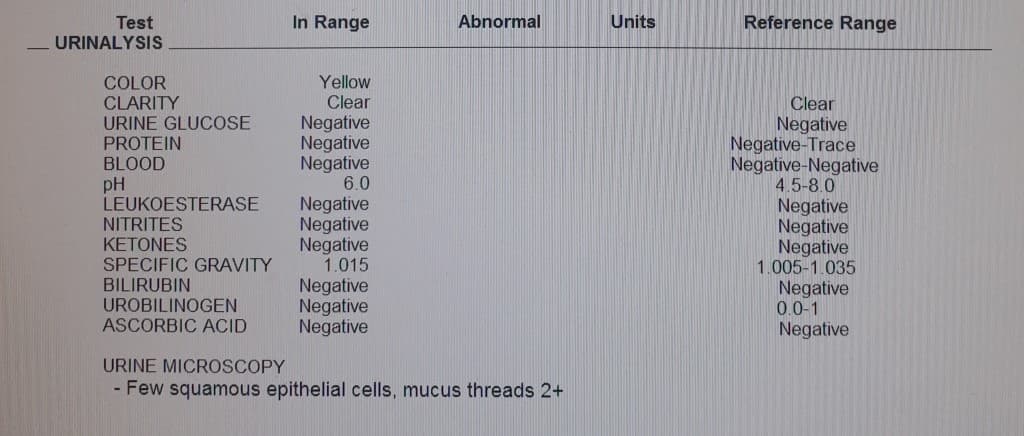
Urinalysis Test Result Pictures
Pictures showing the result of several Urinalysis tests for both men and women of different ages.